Dnmt3a mutation enhances mitochondrial function in blood stem cells, leading to clonal expansion and increased disease risk
Dnmt3a mutation enhances mitochondrial function in blood stem cells, leading to clonal expansion and increased disease risk – WMS – copyright
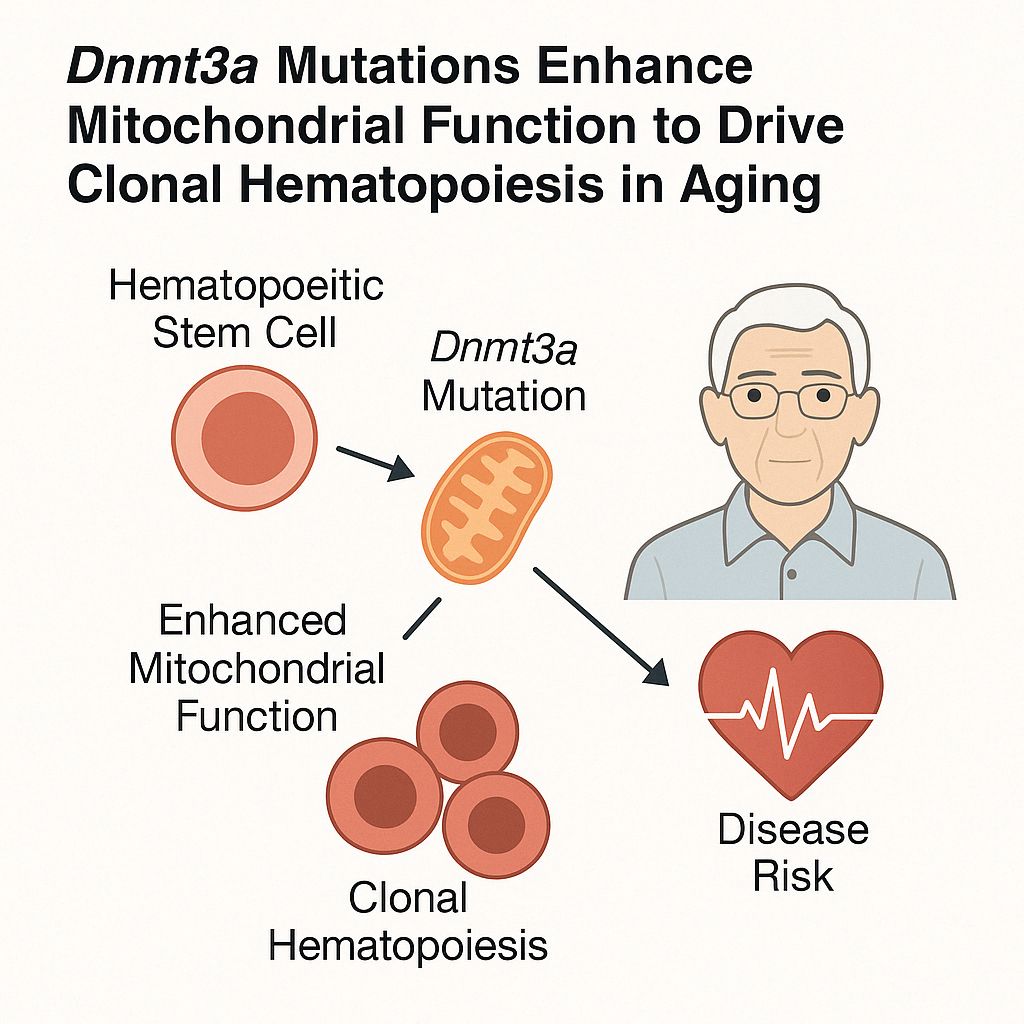
The Jackson Laboratory’s recent study, published on April 16, 2025, in Nature Communications, uncovers how a common age-related mutation in the Dnmt3a gene enhances mitochondrial function in blood stem cells, leading to clonal hematopoiesis—a condition that increases the risk of heart disease, blood cancers, and other illnesses.
Key Findings
- Dnmt3a Mutation and Mitochondrial Enhancement: The Dnmt3a mutation boosts mitochondrial energy production in blood stem cells, granting them a self-renewal advantage.
- Development of Clonal Hematopoiesis: This advantage leads to clonal hematopoiesis, where mutated stem cells dominate, increasing the risk of various diseases.
- Prevalence in Aging Population: Clonal hematopoiesis is common in the elderly, affecting over half of individuals aged 80 and above.
- Inflammatory Impact: Mutated stem cells produce inflammatory molecules that disrupt blood production and weaken the immune system.
- Therapeutic Potential: The study suggests that targeting the enhanced mitochondrial function could be a strategy to prevent or treat clonal hematopoiesis.
These findings show that Dnmt3a-mutated cells rely on enhanced mitochondrial function to dominate,” said senior author Dr. Jennifer Trowbridge. “Targeting this metabolic vulnerability could be a promising strategy to prevent or treat clonal hematopoiesis and its downstream effects.
Marvin Edeas, INSERM, University of Paris, co-organiser of the Targeting Longevity & Mitochondria congress, stated, “This discovery opens new doors to understanding how aging and energy in our cells are connected and how calming overactive mitochondria could help us age more healthily”.
What is DNMT3A?
- It is de novo methyltransferase, meaning it can establish new methylation patterns during development and in adult tissues.
- It plays a crucial role in stem cell differentiation, development, and maintaining genomic stability.
- Mutations in Dnmt3a are commonly found in clonal hematopoiesis, leukemias, and other age-related diseases.
- Recent research shows these mutations can alter mitochondrial function, giving mutant cells a growth advantage.